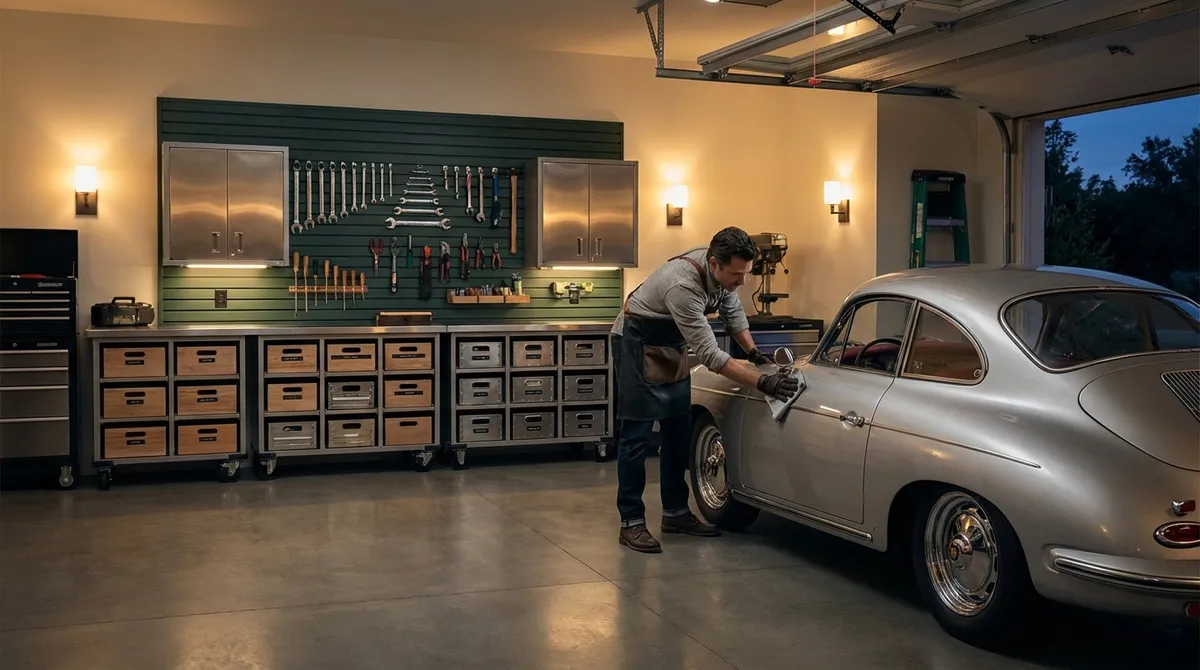
A well‑kept garage is rarely the loudest feature of a distinguished home—but it is often the most revealing. It is the space where precision, order, and reliability are either consistently honored or quietly neglected. For homeowners who expect more than “good enough,” garage maintenance is not a chore; it is an ongoing act of stewardship. Done properly, it protects mechanical integrity, elevates daily convenience, and preserves the quiet dignity of a refined property.
Below, you’ll find a structured approach to garage maintenance built around five exclusive insights—subtle, often overlooked practices that discerning homeowners use to keep this critical space performing at its absolute best.
Reframing the Garage: From Afterthought to Mechanical Nerve Center
In many properties, the garage is the most mechanically dense zone outside of the utility room. It houses the door system, motorized openers, stored equipment, electrical circuits, and often a direct entry into the main residence. Yet it is rarely maintained with the rigor applied to kitchens, HVAC systems, or exterior façades.
For high‑performance homes, that mindset must change. An unbalanced door, a poorly sealed threshold, or a misaligned safety sensor is not merely an inconvenience—it is a vulnerability. It can compromise energy efficiency, security, and, in worst cases, safety. Viewing the garage as a mechanical nerve center clarifies why its maintenance deserves a structured calendar, deliberate inspection routines, and, where appropriate, professional calibration rather than improvised fixes.
By elevating the status of the garage within the broader home‑care strategy, homeowners begin to see how small interventions—precise lubrication, disciplined organization, targeted weather‑proofing—subtly reinforce the overall quality of the property. The result is not just a cleaner garage, but a quieter, more seamless living experience.
Exclusive Insight 1: Treat the Door as Engineered Equipment, Not a Simple Panel
Many homeowners underestimate the complexity of a garage door, seeing only a moving slab of material. In reality, a modern sectional door is an engineered system with calibrated torsion, load distribution, and safety countermeasures. Treating it casually is the fastest way to accelerate wear, invite noise, and risk failure.
Begin with a visual, methodical inspection. With the door closed and opener disconnected (using the emergency release), examine each hinge, roller, bracket, and cable. You are looking for asymmetry: a roller sitting slightly off plumb, a hinge plate beginning to twist, a track that bows outward by a few millimeters. These minor deviations are often the first signal of an impending issue. A premium approach is to document these observations annually—photos, notes, and dates—to identify subtle trends over time rather than react only when something breaks.
For lubrication, resist the temptation to use generic household oils. Instead, use a high‑quality, garage‑door‑specific lubricant on rollers, hinges, and springs, while keeping tracks clean rather than greasy. The goal is not to drown components but to restore controlled, quiet movement. If the door does not stay halfway open when manually raised, or if it slams shut or flies upward, this is no longer a DIY adjustment—it signals a spring balance issue that warrants professional intervention. Discerning homeowners know where attentive observation ends and specialist calibration begins.
Exclusive Insight 2: Engineer the Interior Climate to Protect Both Structure and Storage
Most garage conversations stop at “cold in winter, hot in summer.” High‑expectation homeowners, however, think in terms of controlled microclimates. The garage is a liminal space—neither fully interior nor fully exterior—which makes it uniquely vulnerable to condensation, corrosion, and premature aging of stored items.
Start by addressing air movement before insulation. Simple, elegant measures such as a quiet, wall‑mounted circulation fan on a timer can prevent stagnant air pockets that promote rust on tools, mildew on cardboard, and warping of wooden items. If the garage frequently develops condensation on vehicles or concrete slabs, this is an early indicator of humidity imbalance or temperature differentials between the slab, air, and contents.
Insulation and air sealing should then be treated with the same rigor as a living space: insulated, properly sealed garage doors; weather‑stripped side and back doors; foam gaskets around outlets on shared walls; and attention to the threshold where the house and garage meet. Where climate and usage justify it, a dedicated, appropriately sized mini‑split or dehumidifier can maintain a stable environment, preserving not only mechanical components but also fine storage—bicycles, sporting gear, woodworking equipment, or seasonal decor that would otherwise degrade in a harsh garage climate.
Exclusive Insight 3: Prioritize Silent Operation as a Diagnostic, Not a Luxury
In refined homes, noise is not merely an annoyance—it is data. A properly maintained garage door system should operate with a controlled, muted sound profile: a low, consistent hum from the opener, smooth rolling noise from the door, and no sharp clanks, squeals, or rattles. Homeowners who listen critically to this acoustic signature can detect issues long before they become failures.
Begin by standing inside the garage during operation, with all other ambient sounds minimized. Note where noise concentrates: near the opener, in the tracks, at the joints between panels, or at the floor line. Each zone suggests a different root cause—drive chain tension, misaligned tracks, dry rollers, or an unseated bottom seal. Repeat the observation outside the garage, near the door, and again inside the home at the nearest adjoining wall. Discerning ears will quickly identify intrusive vibration transmitted into the living space.
This attention to sound extends beyond the door. A buzzing fluorescent fixture, a humming outlet, or a rattling storage rack is not trivial; it is an indicator that a connection, fastener, or component is under stress. Upgrading to quieter LED fixtures, using isolation pads beneath heavy equipment, and tightening or re‑anchoring overhead storage systems not only refines the auditory environment but also extends the life expectancy of the components themselves. Silence becomes a standard, not a luxury.
Exclusive Insight 4: Design Storage to Protect the Envelope, Not Just Clear the Floor
Most garage organization advice focuses on maximizing floor space. A more advanced perspective asks a different question: how can storage be arranged so that it protects the building envelope and mechanical systems?
Avoid placing tall shelving units tightly against exterior walls where they trap moisture, conceal early signs of seepage, or allow rodent activity to go unnoticed. Instead, maintain a deliberate inspection gap—just a few inches can reveal early cracks, stains, or rust marks. Keep stored items away from the bottom of drywall where minor water intrusion, melted snow, or a slow leak would otherwise go unseen until significant damage occurs.
Hazardous materials deserve similar scrutiny. Paints, solvents, automotive fluids, and cleaning products should be stored in ventilated, secured cabinets rather than open shelves. This protects indoor air quality, reduces fire risk, and prevents accidental spills from reaching concrete joints or wall framing. For homeowners with premium vehicles or specialty equipment, investing in elevated, load‑rated ceiling storage that is professionally installed can prevent the all‑too‑common sagging or failure of DIY racks. The true goal of storage is not simply neatness—it is to reveal, not conceal, the health of the garage structure.
Exclusive Insight 5: Establish a Formal Garage Maintenance Calendar—And Treat It as Non‑Negotiable
The most refined garage environments rarely happen by accident. They are the product of systems thinking and disciplined repetition. Instead of reactive repairs, discerning homeowners operate from a maintenance calendar that treats the garage as seriously as roofing, HVAC, or major appliances.
A well‑crafted calendar divides care into quarterly and annual tasks. Quarterly, you might perform a safety reversal test of the door (both photo eyes and force settings), sweep and inspect the slab for new cracks or efflorescence, verify that weatherstripping remains supple and intact, and check that any smart opener or keypad remains updated and secure. Annually, a more thorough inspection may include tightening hardware, professionally checking spring tension, servicing the opener drive system, assessing insulation performance, and reviewing storage systems for load, stability, and accessibility.
For those managing multiple properties or complex homes, documenting each maintenance action—date, observations, and any professional service involved—creates a history that is invaluable when selling the property, filing insurance claims, or diagnosing recurring issues. This shift from “fix it when it fails” to “tend it before it falters” is the hallmark of truly elevated garage stewardship.
Conclusion
A garage that performs at a high level does not call attention to itself. It opens quietly, seals cleanly, stores confidently, and integrates seamlessly with the rest of the home. That quiet competence is the result of deliberate, intelligent maintenance—treating the door as engineered equipment, controlling the interior climate, using sound as a diagnostic tool, designing storage to protect the structure, and honoring a formal care schedule.
For homeowners who expect their property to function with the same precision as their finest possessions, the garage is no longer a neglected annex. It becomes what it was always meant to be: a disciplined, finely tuned extension of a well‑run home.
Sources
- [U.S. Department of Energy – Insulation for New and Existing Homes](https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/insulation) – Guidance on insulation and air sealing relevant to garage walls and doors
- [International Association of Certified Home Inspectors – Garage Inspection Guidelines](https://www.nachi.org/gallery/garage.htm) – Professional reference on common garage defects and best‑practice inspection points
- [Consumer Product Safety Commission – Garage Door Safety](https://www.cpsc.gov/Safety-Education/Safety-Education-Centers/Garage-Door-Openers) – Official safety recommendations for garage door operation and maintenance
- [Clopay Garage Doors – Maintenance & Troubleshooting](https://www.clopaydoor.com/garage-door-maintenance) – Manufacturer guidance on caring for modern residential garage doors
- [Department of Energy – Energy Efficient Home Design: Attached Garages](https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/energy-efficient-home-design/energy-efficient-attached-garages) – Details on managing energy, air leakage, and indoor air quality in attached garages
Key Takeaway
The most important thing to remember from this article is that this information can change how you think about Maintenance.